CRISPR, a groundbreaking gene editing technology, is reshaping the landscape of modern medicine and raising profound ethical questions in the process. This innovative tool allows scientists to accurately modify DNA, offering potential cures for genetic diseases like sickle cell anemia, which has long afflicted many. However, as we explore the possibilities of genetic modification, the ethical implications of CRISPR come to the forefront, prompting discussions about health equity and access to these transformative treatments. With the price tag for sickle cell treatments soaring, voices are questioning who will benefit from such advancements and at what cost. As the promise of CRISPR unfolds, it challenges us to consider not only the scientific capabilities but also the moral responsibilities that come with such power.
Gene editing technologies, particularly CRISPR, are at the cutting edge of biomedicine, enabling unprecedented alterations to genetic material. This revolutionary approach opens up numerous avenues for treating inherited conditions, such as sickle cell disease, sparking a debate about the ethical responsibilities associated with genetic engineering. As the implications of these advanced methodologies become more prominent, discussions surrounding the fairness of access to treatments and the potential social consequences arise. The dialogue on health equity becomes essential, particularly as the high costs of genetic modification technologies may limit their accessibility to certain populations. Ultimately, the evolving landscape of genetic intervention solicitous for a balance between innovation and ethical oversight.
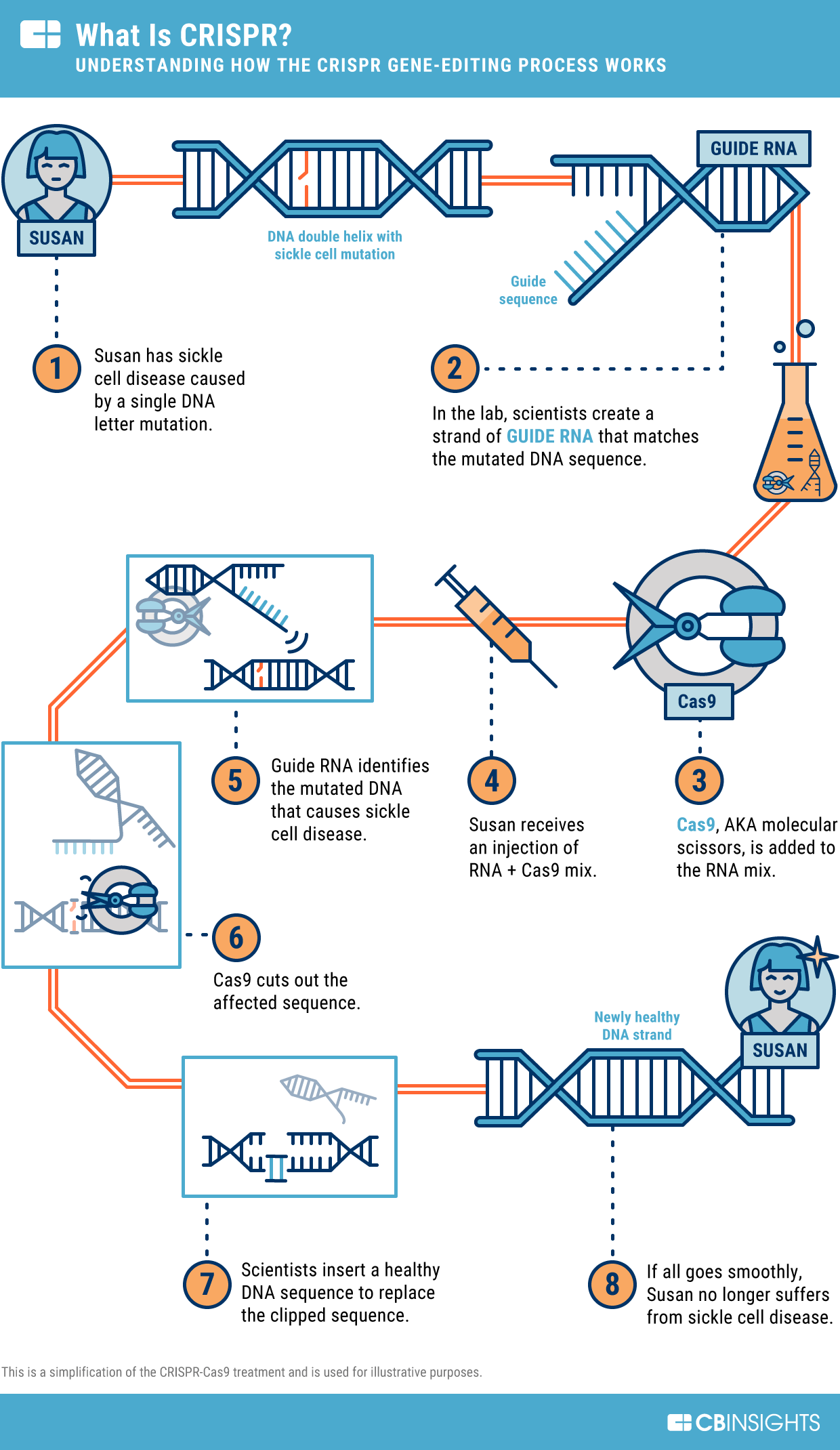
Understanding CRISPR and Its Capabilities
CRISPR, short for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, is a groundbreaking gene editing technology that has revolutionized biomedical research and treatment methods. By allowing precise alterations of DNA within living organisms, CRISPR enables scientists to take on diseases at their genetic root. Particularly in cases such as sickle cell anemia, CRISPR brings hope to millions who suffer from genetic disorders by providing the potential to correct harmful mutations, offering new pathways for treatment.
However, the versatility of CRISPR extends beyond just simple edits; it allows for significant modifications, which raises a range of ethical implications. The ability to manipulate germline genes challenges our understanding of what it means to be human and introduces weighty concerns about ‘designer babies.’ As genetic modification becomes more accessible, discussions about the appropriate use of CRISPR in enhancing human traits rather than just treating illnesses intensify, questioning where we draw the line.
Ethical Implications of CRISPR Technology
The ethical implications of CRISPR technology are vast and complex, leading to intense debates among scientists, ethicists, and society at large. At the heart of these discussions is the question of whether humans should have the authority to edit the genes of future generations. As highlighted by Neal Baer, the potential for misuse exists, such as selecting for specific traits that may not necessarily align with public health interests. The crux of the matter rests on defining the moral boundaries within which gene editing should operate.
Moreover, questions about who should govern gene editing practices are crucial. With technologies advancing rapidly, regulatory frameworks are often lagging behind. Preserving health equity is another cornerstone in managing CRISPR’s implications. Those who can afford gene editing treatments may gain significant health advantages, thereby widening the gap between social classes. This leads to concerns about health justice and whether such innovations truly serve the greater societal good.
CRISPR’s Role in Treating Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease, which affects a significant number of individuals in the U.S., exemplifies the promise and potential of CRISPR technology in clinical applications. By directly targeting the genes responsible for this debilitating condition, researchers have made strides toward potentially curing those affected. The use of CRISPR in correcting the genetic mutations at play offers a glimpse of the future where genetic disorders might become entirely preventable. This not only provides a beacon of hope for patients but also raises expectations for further applications across various genetic conditions.
Despite the exciting potential for CRISPR to cure illnesses such as sickle cell disease, the associated financial implications cannot be ignored. The staggering cost of treatment – around $2.2 million – brings to light profound questions of who will bear the financial burden. Access to cutting-edge treatment options cannot simply be a privilege for those with sufficient resources; it must address issues of equity to ensure that advancements in genetic medicine are available to all, regardless of socio-economic status.
Genetic Modification: A Double-Edged Sword
While genetic modification, particularly through techniques such as CRISPR, offers solutions to heritable diseases, it also presents significant risks. The precision of CRISPR may lead to unintended consequences, as manipulating complex genetic interactions is delicate work. Concerns arise about the long-term effects of these modifications on not just individuals, but entire populations. For instance, altering genes to lower LDL cholesterol might seem beneficial at first, yet the intricate relationships among genes may result in unforeseen side effects that could affect overall health.
Thus, as we move forward with genetic modification technologies, a cautious approach is needed. With great power comes great responsibility, and the implications of altering human DNA extend far beyond individual treatments. Society must grapple with questions of identity, health implications, and the moral responsibilities we bear toward future generations as we continue to harness the capabilities of gene editing.
Health Equity in Gene Editing
The advancements brought about by CRISPR technology must be matched by a strong commitment to health equity. As discussed during the Harvard Science Center presentation, the ability to cure genetic diseases raises critical questions about access to these groundbreaking treatments. If gene editing techniques are not equally available to all populations, we risk exacerbating existing health disparities, leaving marginalized groups without hope for cures that those with resources can afford.
Moreover, health equity discussions must extend beyond mere access to treatments. They should encompass the broader implications of genetic modifications on societal norms, particularly in areas historically characterized by inequities. As CRISPR and similar technologies evolve, proactive measures must be implemented to ensure that advancements contribute positively to health justice and do not unwittingly reinforce societal imbalances.
Genetic Editing and Human Diversity
The dialogue surrounding CRISPR inevitably intersects with notions of human diversity and the value of differences. While the scientific community seeks to alleviate suffering through gene editing, we must also consider the implications of potentially eradicating certain traits or conditions. For instance, the ethical dilemma presented by modifying traits associated with disability — such as being deaf — challenges the societal understanding of what it means to be human and normal.
As articulated by experts during discussions on gene editing, diversity is essential to humanity. The implications of pursuing a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to health through genetic editing could lead to a loss of the rich tapestry that diversity provides. This aspect is crucial to consider as we think about future policies governing CRISPR usage and the prioritization of certain genetic enhancements over others.
The Future of CRISPR Regulation
Effective regulation of CRISPR technology is paramount to prevent misuse and to cultivate public trust. The rapid advancement of gene editing technologies outpaces current legislative frameworks, creating a gap that could lead to unethical applications. Concerns about international oversight, especially from countries with less stringent regulations, amplify the need for a robust global consensus on the ethical use of gene editing.
Future regulations should not only focus on preventing harmful applications but also promote transparency and public engagement. Scientists and ethicists must collaborate with policymakers to create comprehensive guidelines that address the multidimensional challenges posed by CRISPR, balancing scientific innovation with ethical considerations to serve the entire population effectively.
Innovations in Gene Editing Research
As we explore the field of gene editing, it is essential to stay abreast of emerging innovations surrounding CRISPR technology. Each scientific breakthrough not only advances our understanding of genetic diseases but also paves the way for novel therapies that were once deemed impossible. Research into CRISPR applications continues to enable progress in treating conditions like sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis, and even certain types of cancer, transforming the future of healthcare.
In addition, ongoing research necessitates a collaboration between scientists and ethicists to ensure innovations are developed with awareness of their broader societal implications. Each step forward provides opportunities to improve health outcomes while simultaneously raising critical ethical discussions about the direction of genetic modification and its potential impact on future generations.
Public Perception of CRISPR Technology
Public perception plays a vital role in the development and implementation of CRISPR technology. As scientific advancements are made, it is essential to foster a well-informed dialogue with the public to address common misconceptions and educate about the true capabilities and limitations of gene editing. Misunderstandings can lead to fear and resistance, hampering potential benefits from being realized in society.
Engaging with communities to discuss CRISPR’s implications offers the opportunity to highlight both its promise and its ethical challenges. By ensuring public involvement in these discussions, we can collectively navigate the complexities of gene editing while working towards solutions that ensure every individual’s rights and health equity are protected.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CRISPR and how does it relate to gene editing?
CRISPR, or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, is a groundbreaking gene editing technology that allows scientists to precisely alter DNA sequences in living organisms. This technique utilizes a guide RNA to target specific genes for modification, enabling potential cures for genetic disorders, including sickle cell disease. Through CRISPR, researchers can make targeted changes to both somatic and germline genes, leading to significant advancements in genetic modification.
What are the ethical implications of using CRISPR in gene editing?
The ethical implications of CRISPR revolve around the responsibilities and rights associated with altering human genetics. As gene editing can potentially cure conditions like sickle cell anemia, it raises questions about who decides which traits are modified, the impact on health equity, and whether we should intervene in traits deemed ‘normal’ or ‘non-pathological,’ such as Down syndrome. Additionally, issues of access and cost could exacerbate health disparities, necessitating careful ethical considerations.
How does CRISPR technology contribute to sickle cell treatment?
CRISPR technology holds great promise for treating sickle cell disease by enabling precise editing of the patient’s genetic material. By targeting and modifying the genes responsible for this condition, scientists can potentially cure individuals suffering from sickle cell disease. Current applications of CRISPR in this area have shown success in manipulating somatic cells to eliminate the disease’s underlying genetic causes, offering hope for effective treatments.
What potential risks are associated with genetic modification using CRISPR?
While CRISPR offers exciting opportunities for genetic modification, it also poses several risks. These include the possibility of unintended genetic changes, which can lead to unforeseen health consequences. The long-term effects of germline editing are particularly concerning, as changes may be passed on to future generations. Moreover, the lack of regulatory oversight in some countries could lead to unethical applications of CRISPR technology.
How does CRISPR relate to health equity and access to treatments?
CRISPR’s potential to transform medicine raises important questions about health equity. Treatments using CRISPR, such as those designed for sickle cell disease, often come at a high cost, which could limit access for many individuals, especially in low-income populations. This disparity highlights the need for thoughtful policies to ensure that advancements in gene editing technology benefit all segments of society and do not exacerbate existing health inequities.
What are the concerns regarding parental decisions in CRISPR gene editing?
There are significant concerns regarding parental authority in decisions about altering a child’s genetic traits through CRISPR. Questions arise about whether it is ethical for parents to make such profound decisions on behalf of their children, particularly regarding non-life-threatening conditions or genetic traits that contribute to human diversity. These discussions emphasize the need for societal dialogue about the limits and responsibilities accompanying the power of gene editing.
What role does CRISPR play in the future of genetic modification?
CRISPR is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of genetic modification by providing a powerful and precise tool for editing DNA. Its applications range from curing genetic diseases to enhancing agricultural traits. However, as the technology advances, ongoing ethical discussions and careful regulatory measures will be vital to ensure that its potential benefits are realized equitably and safely.
| Key Points |
|---|
| CRISPR offers potential cures for genetic diseases like sickle cell anemia, allowing for significant medical advancements. |
| The ethical ramifications of gene editing are significant; important questions arise about the extent to which we should change human traits. |
| The discussion includes the financial implications of gene therapy and its accessibility, particularly for disadvantaged populations. |
| There are concerns regarding parental choice in genetic modifications and the potential for ‘designer babies.’ |
| Oversight and regulation are critical issues, especially regarding practices in countries with lax laws. |
| The long-term effects and unintended consequences of gene editing pose serious scientific concerns. |
Summary
CRISPR has revolutionized the field of genetic research, offering groundbreaking possibilities for treating diseases like sickle cell anemia. However, this powerful gene editing technology also presents complex ethical dilemmas, from the right to alter human traits to the practicality and fairness of its application. As the conversations around CRISPR evolve, it is vital to address both the benefits and the profound implications of such innovations on society.