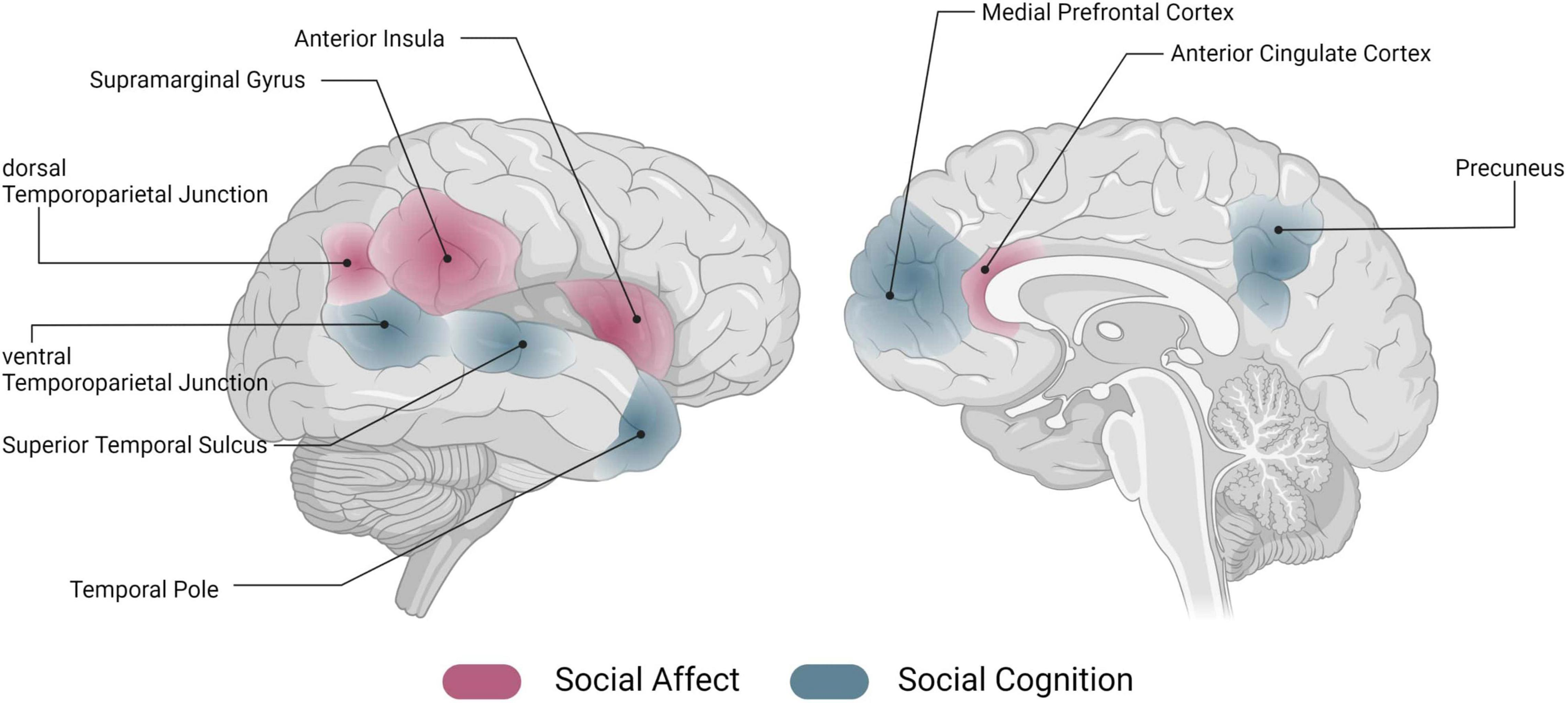
Social interaction neuroscience is emerging as a pivotal field that explores the intricate relationship between our brains and the way we connect with others. Recent research has shed light on the neurological basis for social behavior, revealing that our need for social connection parallels our physiological requirements for food and water. This growing body of evidence highlights the importance of social connection in maintaining mental health, especially as studies have shown the adverse effects of social isolation on psychological well-being. By understanding the mechanisms that compel us to seek out others, scientists hope to better address mental illnesses that stem from social deficits. As our society increasingly grapples with issues related to loneliness, the findings in social interaction neuroscience underscore the vital need for human contact in our lives.
The scientific inquiry into the brain’s role in social behavior encompasses a range of concepts often referred to as the social neuroscience of interaction. This area of study delves into the biological underpinnings that motivate human connections, linking them to essential psychological needs. It emphasizes that our social lives significantly impact our mental health, mirroring the basic human necessities such as warmth, shelter, and nourishment. With rising concerns about the effects of social estrangement, understanding the neurological frameworks that guide social engagement becomes ever more crucial. Ultimately, this exploration may unlock new avenues for addressing the psychological challenges associated with mental illness and social deprivation.
The Neurological Basis for Social Behavior
Understanding the neurological basis for social behavior requires a deep dive into how our brains are wired to prioritize social connection. Research from Ding Liu and his team investigates the underlying neural circuitry that stimulates our social needs, revealing that these needs may be as fundamental as hunger and thirst. The hypothalamus has emerged as a crucial area of interest, where neurons become activated during periods of social deprivation, indicating that our desire for companionship is encoded in our brain’s very fabric.
This exploration into the neurological basis for social behavior is essential for addressing significant societal issues, particularly concerning mental health. With a growing body of evidence linking social isolation to worsening mental health outcomes, understanding how social interaction is regulated in the brain can provide insight into conditions like depression or autism. By identifying specific neural activities that drive our need for social contact, we can work towards more effective interventions for those struggling with mental illnesses related to social needs.
The Importance of Social Connection
Social connection has been recognized as a vital component of human health, significantly impacting our mental and emotional well-being. The U.S. Surgeon General’s declaration of social isolation as a public health concern underscores this importance, drawing attention to how essential it is for individuals to experience meaningful interactions. Researchers like Ding Liu emphasize that social connections are not just advantages but are crucial for survival and overall health, functioning similarly to our biological needs.
Moreover, the significance of social connection is reinforced by studies that highlight both the mental and physical repercussions of social isolation. Engaging with others fulfills not only our innate social needs but also provides psychological benefits that can combat feelings of loneliness and despair. As we navigate an increasingly digital world, where interaction often occurs behind screens, fostering in-person connections becomes even more crucial for mental resistance against social isolation.
Social Isolation and Mental Health Challenges
The correlation between social isolation and mental health challenges is increasingly becoming a focal point in psychiatric research. As isolated individuals often face heightened risks of developing conditions such as depression or anxiety, it is vital to understand the mechanisms involved. Ding Liu’s research indicates that chronic isolation can alter how the brain responds to social situations, potentially leading to a diminished capacity for social interaction and an increased aversion to social settings.
Addressing these issues involves not only therapeutic interventions but also societal changes that promote connectivity among individuals. As we have seen during the pandemic, isolation can severely impact mental health, prompting health professionals to advocate for stronger social bonds and community support systems. The integration of understanding the neurological underpinnings of these relationships can provide a pathway to fostering healthier communities, ultimately improving individual mental health.
Touch: A Fundamental Social Need
Touch plays an integral role in satisfying our social needs, serving as a powerful form of communication that transcends words. Researchers discovered through experiments that, much like food and water, touch is essential for social well-being. The study conducted by Liu’s team demonstrated how mice deprived of social contact preferred environments where they could experience touch, affirming the hypothesis that tactile interaction is crucial for fulfilling social needs.
In humans, the importance of touch is equally significant. Gestures like hugs and handshakes foster connection and emotional support, reinforcing social bonds. As our society becomes more reliant on digital interactions, the lack of physical connection may lead to increased feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can negatively impact mental health. Hence, finding ways to incorporate touch into our daily interactions—even in a technologically driven world—could improve our emotional well-being and strengthen community ties.
Exploring the Roots of Social Interaction
Investigating why we need to socialize opens avenues to better understand the biological and psychological roots of human behavior. Liu’s study suggests that our drive for socialization may stem from fundamental needs similar to those for basic sustenance. By recognizing that social interactions fulfill essential psychological functions, we can appreciate the profound ways our social needs shape our mental health and relationships.
The implications of this research extend beyond individual understanding; they have the potential to guide public health initiatives aimed at reducing social isolation. Encouraging community engagement and providing opportunities for meaningful social interactions can strengthen our collective mental resilience. Understanding these roots not only enhances our approach to mental health care but also cultivates healthier, more cohesive societies.
Mechanisms of Touch in Social Needs Satisfaction
The mechanisms of touch in satisfying social needs are increasingly important in the context of modern life, where virtual interactions often replace physical contact. Liu’s research suggests that sensory inputs, particularly touch, are vital in how we fulfill our social requirements. Experiments with mice showed a strong preference for tactile environments after periods of isolation, indicating that touch is not merely a luxury but a necessity that intimately connects us with others.
For humans, touch acts as a powerful tool for emotional expression and connection. From simple touches during casual greetings to deeper interactions like comforting hugs, the physiological responses triggered by touch can enhance feelings of security and belonging. In light of the rising prevalence of mental health issues linked to social isolation, prioritizing opportunities for physical social interactions could mitigate some of these challenges and promote well-being.
Social Needs and Mental Health Recovery
The understanding of social needs is crucial in the context of mental health recovery. Social behaviors that fulfill these needs can provide essential support structures for individuals grappling with mental illness. By fostering environments where individuals can engage socially, we create pathways for recovery that often rely on the input from family, friends, and community.
Moreover, the insights gained from looking at the neurological basis of social needs can illuminate effective treatment strategies for mental health disorders. Therapeutic approaches that include social interaction as a fundamental component could significantly enhance recovery outcomes. Recognizing that our brains are wired to seek out social connections pushes forward the narrative that social support is integral to holistic mental health care.
Community Building for Mental Well-being
Community building plays a vital role in enhancing mental well-being by addressing the essential social needs of individuals. Public health strategies that promote social interaction can help diminish the devastating effects of isolation on mental health. As highlighted in recent studies, fostering a sense of belonging and connectedness can empower individuals to engage fully in their communities, thus reducing feelings of loneliness and despair.
Efforts to build community through shared activities, social programs, or informal gatherings can create networks of care that significantly bolster mental health resilience. Understanding that social interaction has profound biological roots necessitates collaborative community efforts aimed at making social connections more accessible and rewarding for all, especially in an age where digital interaction may often overshadow physical presence.
Future Directions in Understanding Social Interaction
The future of understanding social interaction lies within continued research efforts focused on elucidating the complexities of how our brains handle social needs. As researchers delve deeper into the neurological foundations, the potential for discovering new insights into mental health treatment strategies can profoundly impact care. Questions regarding how the brain processes social cues and the role of tactile sensations remain at the forefront of this evolving science.
Furthermore, expanding research that includes diverse populations can provide a more comprehensive understanding of how social needs manifest across different cultural contexts. By incorporating interdisciplinary approaches, we can enrich our grasp of social interaction’s importance, thereby enhancing mental health interventions and promoting healthier, more connected societies. Increasing awareness and supporting research initiatives will enable us to effectively address the pressing social factors that influence mental health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neurological basis for social behavior according to recent research?
Recent studies, including research from the Dulac lab, indicate that social behavior is governed by specific neurons in the hypothalamus, similar to those responsible for hunger and thirst. These neurons activate during periods of social deprivation, highlighting the neurological basis for social interaction as a fundamental human need.
How does social isolation impact mental health based on findings in social interaction neuroscience?
Social isolation has been identified as a significant public health concern, with profound implications for mental health. Research shows that prolonged isolation can lead to debilitating mental illnesses, such as depression and anxiety, underscoring the importance of social connection for psychological well-being.
Why is touch considered essential for fulfilling social needs in neuroscience studies?
Studies indicate that touch plays a crucial role in fulfilling social needs. Mice experiments revealed that even when they could see and hear each other, lack of physical contact led to similar effects as social isolation. This suggests that tactile interactions, like hugging or handshakes in humans, are vital for healthy social bonds.
What is the connection between mental illness and social needs in the context of neuroscience?
The connection between mental illness and social needs is significant; individuals with conditions such as autism, depression, or schizophrenia often struggle with social interactions. Understanding the neurological basis of these interactions can offer insights into treatment and support for these individuals.
How do researchers study the importance of social connection in neuroscience?
Researchers study the importance of social connection by examining neuronal activity during social interactions and isolation. By creating experimental scenarios that simulate social deprivation in animals, they observe the neurological responses that indicate the need for social engagement, contributing to our understanding of social behavior’s underlying mechanisms.
What implications do findings about social interaction neuroscience have for society?
Findings in social interaction neuroscience emphasize the necessity of social connections for overall health, suggesting that as we increasingly engage online, we may miss out on physical interactions essential for mental health. This research can inform public health initiatives aimed at reducing social isolation in communities.
What role does the hypothalamus play in social interactions according to recent research?
The hypothalamus plays a key role in regulating social interactions by controlling neural circuitry that responds to social deprivation, similar to its functions in regulating basic needs such as hunger and thirst. This dual role illustrates the essential nature of social connections for sustaining both physical and mental health.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Health professionals recognize social connection as essential as basic needs like food and water. |
| Research led by Ding Liu uncovers the neurological basis for social needs, focusing on the hypothalamus. |
| Study suggests that social behavior may be driven by avoiding negative experiences rather than seeking pleasure. |
| The study observed behaviors in mice during isolation and reunion, noting the importance of physical touch. |
| Findings indicate that social needs are critical for mental health, paralleling needs for food, water, and sleep. |
Summary
Social interaction neuroscience is a rapidly evolving field that elucidates the neurological mechanisms underlying our intrinsic need for social connection. Understanding how our brain reacts to social interactions, similar to our responses to hunger or thirst, opens up essential avenues for addressing mental health issues. As research continues, it highlights the intrinsic role of touch and physical presence in fostering healthy social relationships, emphasizing their importance in both animal and human behavior.