Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked a heated debate among nutrition experts, as many people experience intense sugar cravings that can lead to habitual overconsumption of sweet foods. While it isn’t classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, the health effects of sugar—including increased cravings and compulsive eating behaviors—suggest it can create a strong psychological pull. The prevalence of sugar in processed foods exacerbates these cravings, making it difficult for individuals to moderate their sugar intake effectively. Understanding the nuances of sugar in our diet, alongside the impact of added sugars in our everyday meals, is crucial for promoting healthier eating habits.
The inquiry around the addictive properties of sugar mirrors discussions about other substances in our diet that can lead to dependency. Terms like sugar cravings and sugar addiction have become part of our culinary vernacular, highlighting a potential struggle many face regarding sweet treats. Despite the absence of clinical classification as a true addiction, the emotional and physical effects of consuming high quantities of sugar can be profound. Processed foods, often loaded with sugar, play a significant role in this dynamic, pushing individuals toward unhealthy eating patterns. By examining these relationships, we can better grasp the implications of sugar on our overall health and wellbeing.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
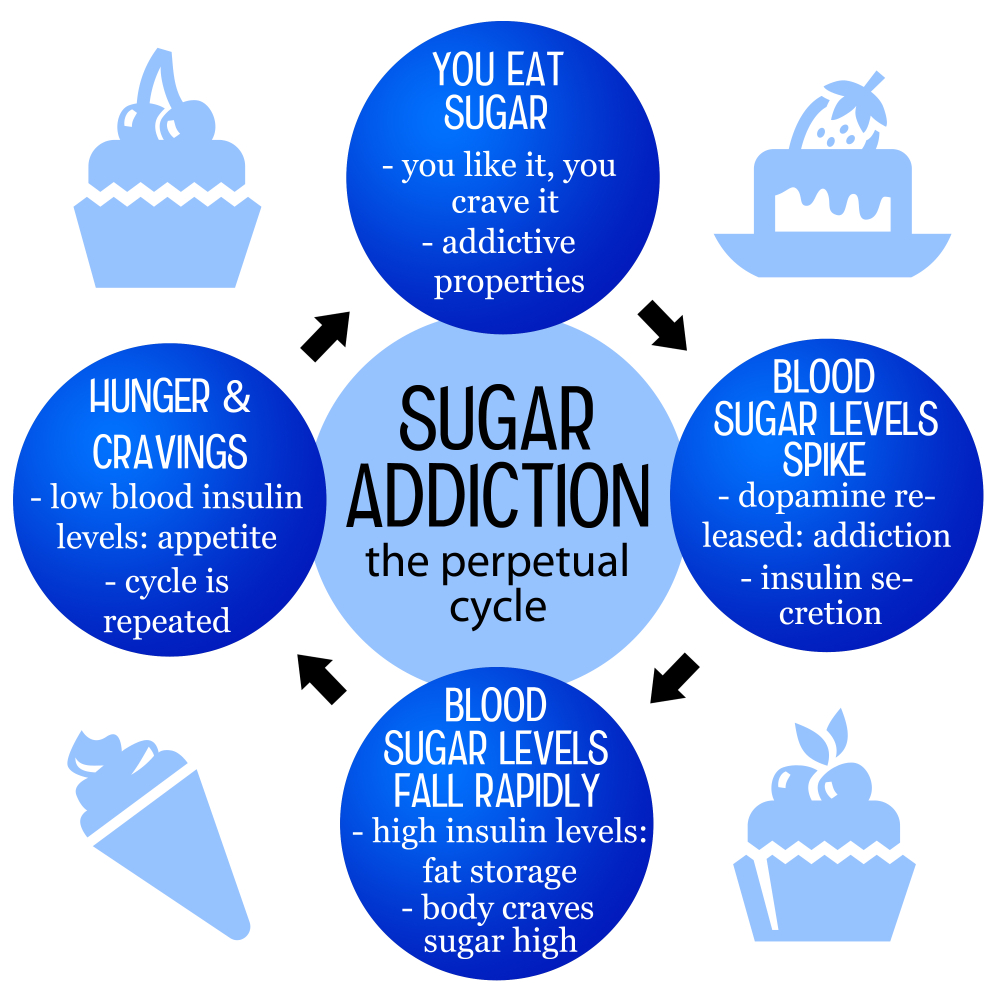
The concept of sugar addiction is complex and often misunderstood. While sugar can trigger cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria used to define substances like nicotine or alcohol as addictive. According to nutrition experts, physical reactions to sugar, such as changes in mood or energy levels after consumption, are very real, but they may not equate to the severe withdrawal symptoms associated with drug addiction. It highlights the unique nature of sugar as a food source that the body needs, as opposed to a substance that can be entirely eliminated.
Developed countries face a challenge with sugar consumption, primarily due to the prevalence of ultra-processed foods that contain high levels of added sugars alongside unhealthy fats and sodium. These foods stir up intense cravings because they are specifically designed to be appealing. As individuals become accustomed to these high levels of sugar and then attempt to cut back, they may encounter withdrawal-like symptoms including irritability and headaches. This creates a cycle where the body becomes reliant on sugar for quick energy boosts, making moderation crucial for managing sugar intake.
The Health Effects of Excess Sugar Consumption
High sugar consumption is linked to a range of health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, which far exceeds the recommended limits set by the American Heart Association. Excessive sugar intake contributes to weight gain through additional caloric intake and can also lead to insulin resistance, which is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes. Lowering sugar in the diet can bring about a significant positive impact on health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases associated with poor diet.
Moreover, the psychological impact of sugar consumption shouldn’t be ignored. Processed foods rich in added sugars can create preferences for sweet flavors over healthier options, leading to imbalanced diets. Understanding these health effects emphasizes the importance of monitoring one’s sugar intake and making conscious choices regarding food. Instead of equating sugar with addictive substances, focusing on moderation and mindful eating can help mitigate health risks while still allowing individuals to enjoy sugar in a responsible manner.
Sugar Cravings and Behavioral Patterns
Sugar cravings can often mimic the behaviors associated with addiction, leading many to wonder about its potential addictive properties. People frequently experience uncontrollable urges to reach for sweets, particularly in response to stress or emotional triggers. This highlights a behavioral component that can be challenging to navigate. Recognizing these patterns can play a key role in managing sugar intake and establishing healthier eating habits. Instead of avoiding sugar altogether, individuals might find it beneficial to learn how to satisfy their sweet cravings with healthier alternatives, such as fruits.
Fostering an awareness of sugar’s role in diet can also lead to better decision-making. Acknowledging when cravings arise can empower individuals to choose snacks that are not only pleasurable but also nutritious. By incorporating natural sources of sugar, like fruits, into their diets, individuals can curb their cravings while still enjoying sweetness in moderation. Establishing healthier habits is a gradual process, and understanding the mechanisms behind sugar cravings is key to overcoming them.
Navigating Processed Foods and Sugar Intake
The abundance of processed foods in modern diets presents a significant challenge for managing sugar intake. These foods are often engineered to enhance flavor and palatability, making them hard to resist. The presence of high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium in these products can lead to habitual consumption, complicating efforts to cut back on sugar. Understanding the ingredients and nutritional values listed on food labels is vital for making informed choices about what to eat.
Parents and individuals should be particularly vigilant about the sugar content in processed snacks and drinks, as these can contribute significantly to daily sugar consumption without providing nutritional benefits. Simple strategies, such as planning meals that are primarily based on whole foods and limiting processed options, can help manage overall sugar intake. By being proactive in dietary choices, individuals can reduce their reliance on processed foods and improve their overall health.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
Despite the concerns surrounding sugar, it is important to acknowledge its place in a balanced diet. Natural sugars found in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy products provide not only energy but also essential nutrients. These foods should form the basis of our diet, ensuring we receive adequate vitamins and minerals while still allowing for occasional indulgences. Moderation is key; enjoying sweets in smaller amounts as part of a diverse and nutritious diet can lead to a healthier relationship with food.
By focusing on the quality of sugar sources rather than attempting to eliminate sugar entirely, individuals can maintain a balanced approach to eating. Eliminating sugar can backfire, leading to heightened cravings and potentially unhealthy eating behaviors. Instead, emphasizing the enjoyment of naturally sweet foods can provide satisfaction without compromising health. Mindful consumption of sugar balances pleasure with nutritional value, promoting a long-term healthy lifestyle.
Gradually Reducing Sugar in Your Diet
For those looking to cut down on sugar, a gradual approach can prove more effective than going cold turkey. As outlined by nutrition experts, abruptly eliminating sugar can lead to intense cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms, making it more challenging to sustain dietary changes. Instead, individuals should focus on slowly reducing their intake of added sugars by substituting high-sugar snacks with healthier options. For instance, swapping out candy for fruit can satisfy sweet cravings while providing more nutritional benefits.
Additionally, experimenting with naturally sweet flavors in cooking and baking can help transition away from reliance on processed sugary foods. Incorporating spices like cinnamon or vanilla can enhance sweetness without the added sugar. By taking manageable steps and remaining patient, individuals can develop a healthier relationship with sugar and learn to enjoy it in moderation.
The Importance of Reading Food Labels
Understanding sugar content in food products necessitates reading food labels carefully. Many processed foods contain hidden sugars that can significantly increase daily intake without awareness. Ingredients can be misleading, and terms like ‘high fructose corn syrup’ or ‘agave nectar’ may not immediately register as added sugars. Being informed about these subtleties allows consumers to make healthier choices and select products with lower sugar content.
Moreover, food labels also provide crucial information regarding nutritional value, serving sizes, and overall caloric content. By paying attention to these details, individuals can better monitor their sugar intake and remain within recommended guidelines. Awareness of food ingredients empowers consumers, leading to healthier decisions and an overall improvement in dietary habits.
Sugar and Emotional Well-being
Sugar’s impact extends beyond physical health—it can also affect emotional well-being. Many turn to sugary snacks for comfort during stressful situations, creating a cycle of reliance and emotional overeating. This connection highlights the psychological aspect of sugar consumption, as comfort foods can offer a temporary reprieve from stress but may lead to guilt and unhealthy eating patterns. Recognizing this emotional tie can assist individuals in addressing cravings more effectively.
To promote emotional well-being while managing sugar intake, individuals can seek healthier coping mechanisms. Activities such as exercise, mindfulness, and engaging in hobbies can serve as positive distractions from sugar cravings. By finding alternative ways to manage emotions, individuals can reduce reliance on sugar as a source of comfort.
Reframing Your Relationship with Sugar
Changing how we view sugar intake can lead to healthier behaviors. Instead of vilifying sugar as an enemy, reframing it as a part of life that should be enjoyed in moderation can encourage a more positive relationship with food. Acknowledging sugar’s role as an energy source can transform our approach to cravings and limits, allowing for occasional indulgences without the guilt attached to them.
This shift in mindset fosters a healthier, more balanced diet where sugar is consumed as part of a diverse array of food choices. Encouraging a focus on the nutritional benefits of whole foods and the joy of enjoying sweet flavors in moderation promotes a sustainable approach to eating that supports both physical and emotional health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like drugs or alcohol?
While sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like drugs or alcohol. The effects of sugar can mimic addiction, but they are generally less severe.
What are sugar cravings and how do they relate to sugar addiction?
Sugar cravings are intense desires for sugary foods, which can be a sign of habitual consumption of processed foods with added sugar. These cravings can be likened to addictive behaviors but do not meet the clinical criteria for substance addiction.
What are the health effects of sugar consumption?
Excessive sugar intake is linked to health issues like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Moderate sugar consumption from whole foods can be part of a healthy diet, but added sugars in processed foods should be limited.
How can I manage sugar cravings without experiencing withdrawal symptoms?
To manage sugar cravings, it’s better to gradually reduce added sugar in your diet rather than going cold turkey. Incorporating more whole foods that naturally contain sugar, like fruits, can help you satisfy your sweet tooth more healthily.
How does sugar in the diet affect our overall health?
Sugar in moderation can enhance flavor and pleasure in our diet, but excessive consumption—especially from processed foods—can lead to significant health issues. Monitoring your sugar intake is essential for maintaining good health.
Are processed foods to blame for sugar addiction?
Yes, ultra-processed foods often contain high levels of added sugar and unhealthy fats, which can trigger cravings and habitual consumption patterns, making it difficult to moderate intake.
What recommendations does the American Heart Association provide regarding added sugar?
The American Heart Association recommends that men limit their intake to no more than 9 teaspoons, women to 6 teaspoons, and children to even less to promote overall health and prevent sugar-related issues.
Can a little sugar be healthy for us?
Yes, incorporating sugar from natural sources like fruits and dairy in moderation can be healthful. The key is balancing sugar intake and being mindful of added sugars in processed foods.
What steps can I take to reduce sugar in my diet?
To reduce sugar intake, read food labels, choose whole foods, and gradually lower the amount of added sugar you consume. This gradual approach can help prevent withdrawal-like symptoms associated with cutting out sugar abruptly.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Is Sugar Addictive? | The debate continues; sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like nicotine or alcohol but has addictive qualities. |
| Nutrition Research Perspective | Frank Hu, a nutrition expert from Harvard, highlights that sugar increases cravings but lacks formal addiction classification. |
| Effects of Sugar Consumption | Consumption of ultra-processed foods leads to cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms if consumption suddenly ceases. |
| Sugar in Our Diet | Sugar is present in many essential foods (fruits, vegetables, dairy), making it different from drugs that can be removed completely from the diet. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | The American Heart Association advises limits on added sugar: 9 tsp for men, 6 tsp for women, much less for children. |
| Mindful Consumption | Encouraged to monitor sugar intake and gradually reduce consumption rather than quit cold turkey. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The consensus among experts is that while sugar exhibits some addictive qualities, it is not officially classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. This distinction is important because sugar is naturally present in many healthy foods, and it’s possible to incorporate it into a balanced diet without negative health implications. The challenge lies in the excessive amount of added sugars in many processed foods, which can lead to cravings and adverse health effects if consumed in high quantities. Therefore, it’s crucial to be mindful of sugar intake and to make gradual changes rather than drastic eliminations. Understanding the nature of sugar can help individuals enjoy its sweetness while maintaining a healthy lifestyle.