Alzheimer’s detection is becoming increasingly vital as researchers uncover new ways to identify cognitive decline earlier than ever. Recent advancements suggest that the olfactory system—or sense of smell—can serve as a powerful tool in early detection of Alzheimer’s disease, ultimately allowing for timely intervention. The innovative olfactory tests developed by Harvard-affiliated Mass General Brigham provide a simple yet effective way for individuals to assess their own cognitive health from the comfort of home. By recognizing cognitive impairment signs through the ability to identify and remember odors, this at-home test can help flag those at risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases long before symptoms surface. As the research progresses, the potential for transforming Alzheimer’s detection into a noninvasive, accessible process becomes ever clearer.
In the realm of identifying Alzheimer’s, various terms are often used interchangeably to discuss this critical issue. The identification of early signs of Alzheimer’s disease and related neurodegenerative conditions is crucial for proactive health management. For instance, home tests for cognitive decline, like the emerging olfactory assessments, play a pivotal role in evaluating an individual’s mental acuity and memory capabilities. These assessments can reveal subtle changes in cognitive functioning that may go unnoticed, reflecting a growing focus on early intervention strategies for those experiencing cognitive impairment. Understanding these alternative approaches further emphasizes the importance of timely Alzheimer’s detection in maintaining brain health.
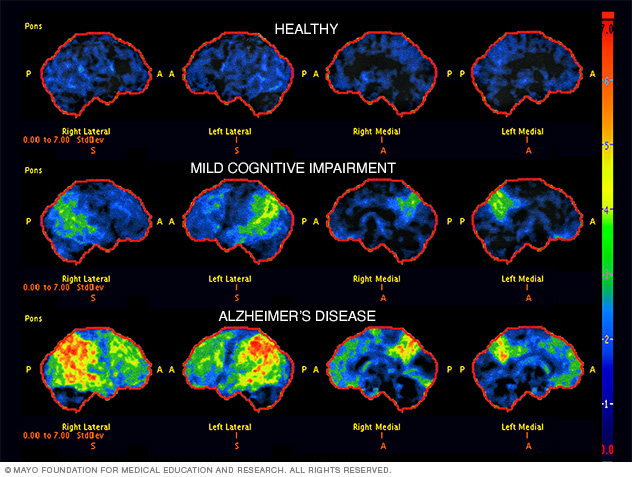
The Importance of Early Detection in Alzheimer’s Disease
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for effective intervention and treatment strategies. With neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, symptoms often manifest years after the underlying pathology has begun. By utilizing innovative methods for early detection, such as olfactory tests, researchers aim to identify cognitive impairment signs before more severe symptoms, like memory loss, become apparent. Studies have shown that cognitive deficits can start years before clinical symptoms arise, making early diagnosis vital for improving patient outcomes.
The adoption of home-based tests for early detection marks a significant advancement in Alzheimer’s research. Individuals can assess their olfactory function—a potential early marker of cognitive decline—without needing to visit a medical facility. This accessibility promotes increased testing rates, enabling more people to be monitored for signs of cognitive impairment. As the understanding of Alzheimer’s disease evolves, tools that provide early detection can lead to proactive management of the condition, ultimately delaying progression and enhancing the quality of life for individuals at risk.
Olfactory Tests: A New Frontier in Alzheimer’s Detection
Olfactory tests represent a novel approach to Alzheimer’s detection, leveraging the sense of smell to assess cognitive health. Recent studies conducted by researchers at Mass General Brigham have indicated a strong correlation between olfactory dysfunction and cognitive impairment. These tests focus on individuals’ ability to identify, discriminate, and remember different odors, where lower scores often indicate the presence of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s. Identifying these early signs through such tests can lead to earlier interventions and more tailored treatments.
By engaging participants, both English- and Spanish-speaking, the olfactory test has proved to be universally effective, emphasizing its potential in diverse populations. Part of the significance lies in its non-invasive nature and the feasibility of conducting the tests at home. This factor not only reduces the barriers to testing but also allows for broader participation in research studies aimed at uncovering the links between olfactory dysfunction and cognitive decline. As the understanding of these connections deepens, olfactory tests could become a commonplace method for Alzheimer’s detection in clinical settings.
Cognitive Impairment Signs: Recognizing the Red Flags
Cognitive impairment can manifest in various ways, and recognizing these signs early is paramount for effective intervention. Symptoms may include difficulty remembering recent events, confusion with dates, or challenges in following conversations. Such cognitive changes can be subtle, and many individuals may not recognize their significance until they impact daily life. The development of screening tools, like olfactory tests, has the potential to enhance awareness and understanding of these cognitive impairment signs among both healthcare providers and the general public.
Understanding the signs of cognitive impairment is particularly relevant given the aging population. As the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease rises, spreading awareness about the early indicators of cognitive decline is crucial. Educational campaigns emphasizing the importance of monitoring cognitive health and utilizing tests for early detection could lead to timely diagnoses. Alongside olfactory testing, other methods should be explored to create comprehensive screening protocols that incorporate various cognitive assessments, ensuring individuals can receive appropriate care at early stages.
Home Test Alzheimer’s: Empowering Individuals and Families
The rise of home tests for Alzheimer’s detection empowers individuals and families by fostering a proactive approach to cognitive health. Tools that allow for self-assessment are invaluable in reducing the stigma associated with memory concerns. Home tests, such as the at-home olfactory evaluation developed in recent studies, enable users to measure their cognitive abilities discreetly. This not only facilitates early detection but also encourages family members to engage in conversations about cognitive health and potential interventions.
As families become more informed about Alzheimer’s disease and the related cognitive deficits, they can better support loved ones who are experiencing symptoms. This supportive environment allows for timely discussions about seeking professional evaluation and treatment options. The flexibility and accessibility of home testing can lead to increased awareness of neurodegenerative diseases and their risk factors, creating a cultural shift towards prioritizing brain health among individuals in all stages of life.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Growing Concern
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, present unique challenges due to their progressive nature and impact on cognitive function. As global populations age, the prevalence of these disorders is expected to rise significantly, highlighting the urgent need for early detection methods. Researchers are increasingly focusing on the link between sensory deficits, like olfactory dysfunction, and neurodegeneration to identify at-risk individuals earlier, paving the way for intervention strategies that could improve life quality before severe symptoms actually arise.
Interdisciplinary research efforts are essential in tackling the complexities of neurodegenerative diseases. By incorporating findings from various fields, such as neurology, psychology, and olfactory studies, researchers can develop comprehensive models for understanding these conditions. The integration of home testing, such as olfactory assessments, can be a part of a multi-faceted approach to identifying at-risk individuals and monitoring changes in cognitive health over time. Such collaboration can help expand knowledge and foster innovative solutions in the battle against neurodegenerative diseases.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research: Innovative Approaches
The future of Alzheimer’s research is poised for groundbreaking advancements, driven by innovative testing methods and a deeper understanding of the disease’s pathology. Tools like olfactory tests are just the beginning in developing non-invasive, user-friendly assessments. As researchers refine these techniques, we can expect to see a paradigm shift in how we approach dementia diagnosis and intervention. Early detection will not only change individual outcomes but will also create opportunities for widespread education about cognitive health.
As Alzheimer’s research continues to evolve, interdisciplinary collaborations between neuroscientists, psychologists, and technologists will be paramount. These partnerships can harness new technologies to enhance testing methodologies, leading to earlier and more accurate assessments of cognitive health. The potential for improved outcomes through timely intervention based on evidence from these studies can revolutionize care for Alzheimer’s patients, ultimately aiming to halt or even reverse the progression of this debilitating disease.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Alzheimer’s Detection
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease, ensuring patients receive timely assessments and appropriate care. As the research community identifies new markers for cognitive impairment, it becomes the responsibility of healthcare systems to integrate these findings into clinical practice. By utilizing tools such as olfactory tests, providers can enhance their diagnostic capabilities, paving the way for earlier interventions that can slow disease progression.
Furthermore, patient education is a crucial aspect of Alzheimer’s detection. Healthcare providers must facilitate conversations about cognitive health with their patients and families, helping them recognize the importance of monitoring cognitive changes. As public awareness about Alzheimer’s disease and its early signs grows, healthcare professionals must remain at the forefront, guiding individuals through preventive measures and treatment options available to enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Public Awareness and Early Detection Strategies
Promoting public awareness around Alzheimer’s disease is essential for improving early detection rates. By educating the community on the importance of cognitive health and recognizing early warning signs, individuals can take a more proactive approach to their well-being. Awareness campaigns can emphasize how tools like olfactory tests can assist in identifying cognitive impairment early on, ultimately empowering individuals to seek the necessary assessments and treatments.
Communities can also benefit from programs that offer informative sessions on neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s. This kind of engagement fosters a supportive network where families can share experiences and resources related to cognitive health. Additionally, by incorporating regular brain health checks, including non-invasive tests, society can normalize conversations about cognitive impairment, allowing everyone to better understand the significance of maintaining cognitive wellness throughout their lives.
Potential for Integrated Care Models
As new methods for Alzheimer’s detection continue to emerge, the potential for integrated care models becomes increasingly evident. By combining olfactory tests and other cognitive assessments into a cohesive strategy, healthcare providers can create a more comprehensive framework for patient management. This integration allows for a holistic view of an individual’s cognitive health, taking into account various factors that contribute to neurodegenerative diseases.
Moreover, integrated care models can facilitate better communication among healthcare professionals. This team-oriented approach ensures that healthcare providers, specialists, and caregivers collaborate effectively, allowing for coordinated interventions tailored to the unique needs of Alzheimer’s patients. As the landscape of Alzheimer’s research evolves, these integrated models will be crucial in improving patient outcomes and enhancing the overall quality of care for those affected by cognitive decline.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of early detection of Alzheimer’s disease?
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial because it allows for timely intervention and management of symptoms before significant cognitive decline occurs. Understanding cognitive impairment signs can facilitate proactive treatment options, enhancing the quality of life for individuals at risk as they prepare for possible future challenges.
How do olfactory tests aid in the detection of Alzheimer’s disease?
Olfactory tests can help in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease by assessing an individual’s ability to identify and remember odors. Research indicates that those with cognitive impairment often score lower in these tests compared to cognitively healthy individuals, making olfactory dysfunction a potential early warning sign for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Can I perform an at-home test for Alzheimer’s detection?
Yes, there are at-home tests for Alzheimer’s detection, such as the olfactory test developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham. This test, which involves sniffing different odors, can help identify those at risk of cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s years before the onset of noticeable symptoms.
What are the common signs of cognitive impairment related to Alzheimer’s?
Common signs of cognitive impairment related to Alzheimer’s include memory loss, difficulty completing familiar tasks, challenges in planning or problem-solving, confusion with time or place, and changes in mood or personality. Notably, decreased ability to identify and remember odors may also indicate early cognitive decline.
What role does the sense of smell play in Alzheimer’s detection?
The sense of smell plays a significant role in Alzheimer’s detection because research has found that olfactory dysfunction can be an early indicator of neurodegenerative diseases. A decline in olfactory capabilities may signal cognitive impairment, prompting further assessments for conditions like Alzheimer’s.
What is the Aromha Brain Health Test and how does it relate to Alzheimer’s detection?
The Aromha Brain Health Test is an olfactory assessment tool designed to evaluate a participant’s ability to identify and remember smells. It relates to Alzheimer’s detection by helping to identify individuals who may be at risk of cognitive impairment, potentially allowing for early intervention in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| New Olfactory Test for Alzheimer’s | Mass General Brigham developed an at-home olfactory test to detect risks of Alzheimer’s disease before symptoms surface. |
| Importance of Early Detection | The ability to detect cognitive impairment early could lead to interventions years before memory symptoms appear, potentially improving patient outcomes. |
| Group Composition | Participants included English- and Spanish-speaking individuals with cognitive complaints and those with mild cognitive impairment. |
| Impact of Olfactory Function | The study found that older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower in odor discrimination and identification tests compared to their cognitively normal peers. |
| Future Research Directions | Further studies could integrate neuropsychological testing and track patients over time to validate the tool’s predictive ability for cognitive decline. |
| Funding | The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, ensuring credible support for the research. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s detection plays a crucial role in improving patient care by allowing for early interventions. The development of a home-based olfactory test by researchers at Mass General Brigham is a promising advancement in this field. By measuring an individual’s ability to identify and discriminate odors, this innovative method aids in revealing potential cognitive decline before the onset of typical Alzheimer’s symptoms. The findings underscore the necessity of continuous research in identifying effective early detection tools for neurodegenerative diseases, paving the way for better management and treatment options.